1. Permission
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CALL_LOG" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_CALL_LOG" />
2. Source
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public static final String MESSAGE_TYPE_INBOX = "1";
public static final String MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT = "2";
public static final String MESSAGE_TYPE_CONVERSATIONS = "3";
public static final String MESSAGE_TYPE_NEW = "new";
final static private String[] CALL_PROJECTION = { CallLog.Calls.TYPE,
CallLog.Calls.CACHED_NAME, CallLog.Calls.NUMBER,
CallLog.Calls.DATE, CallLog.Calls.DURATION };
private static final String TAG = "Victor-Manage_Clique";
private Cursor getCallHistoryCursor(Context context) {
Cursor cursor = context.getContentResolver().query(
CallLog.Calls.CONTENT_URI, CALL_PROJECTION,
null, null, CallLog.Calls.DEFAULT_SORT_ORDER);
return cursor;
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
callLog();
}
private void callLog() {
int callcount = 0;
String callname = "";
String calltype = "";
String calllog = "";
Cursor curCallLog = getCallHistoryCursor(this);
Log.i( TAG , "processSend() - 1");
// Log.i( TAG , "curCallLog: " + curCallLog.getCount());
if (curCallLog.moveToFirst() && curCallLog.getCount() > 0) {
while (curCallLog.isAfterLast() == false) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
if (curCallLog.getString(curCallLog
.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.TYPE)).equals(MESSAGE_TYPE_INBOX)){
calltype = "수신";
}
else if (curCallLog.getString(curCallLog
.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.TYPE)).equals(MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT)){
calltype = "발신";
}
else if (curCallLog.getString(curCallLog
.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.TYPE)).equals(MESSAGE_TYPE_CONVERSATIONS)){
calltype = "부재중";
}
if (curCallLog.getString(curCallLog
.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.CACHED_NAME)) == null) {
callname = "NoName";
}
else {
callname = curCallLog.getString(curCallLog
.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.CACHED_NAME));
}
sb.append(timeToString(curCallLog.getLong(curCallLog
.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.DATE))));
sb.append("\t").append(calltype);
sb.append("\t").append(callname);
sb.append("\t").append(curCallLog.getString(curCallLog.getColumnIndex(CallLog.Calls.NUMBER)));
curCallLog.moveToNext();
String backupData = sb.toString();
callcount++;
Log.i("call history[", sb.toString());
}
}
}
private String timeToString(Long time) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String date = simpleFormat.format(new Date(time));
return date;
}
}
Showing posts with label android. Show all posts
Showing posts with label android. Show all posts
Monday, December 23, 2013
Sunday, December 22, 2013
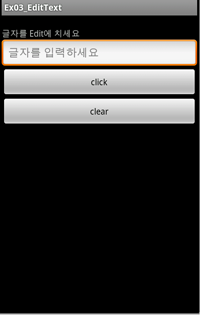
Android: How to use Edittext in android
- JAVA
public class Ex03_EditTextActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button button = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button1);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
Button button1 = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button2);
button1.setOnClickListener(this);
}
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button button = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button1);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
Button button1 = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.Button2);
button1.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
EditText editText = (EditText)this.findViewById(R.id.Edit1);
TextView textView = (TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.TextView1);
switch(arg0.getId()){
case R.id.Button1: // Input text to textView from editText
String al1 = editText.getText().toString();
textView.setText(al1);
break;
case R.id.Button2: // Clear All
editText.setText("");
textView.setText("");
break;
}
}
}
-xml 소스
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="글자를 Edit에 치세요" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/Edit1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="글자를 입력하세요" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/Button1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="click" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/Button2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="clear" />
</LinearLayout>
- Display
Android: How to use Listview in android
public class MainActivity extends Activity { String[] mData = {"A", "B", "C", "D"}; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main_activity);
ListView mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list); ArrayAdapter adapter
= new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, mData); mListView .setAdapter(adapter); } }
Friday, December 20, 2013
Android: How to build AOSP (Android Full Source)
·
make -j24 -k 2>&1 | tee
android.log
o
-j
:
Allow N jobs at once
:
Use to raise compile speed
:
For example, if the number of CPU is 4, as create process 4 by command -j4,
build speed can raise.
o
-k
:
--keep-going
:
Keep going when some targets can’t made (Keep going run build although error
occurred)
:
If you want to check error when error occurred immediately, you don’t need to
use this command.
o
2>&1
:
n >&m
:
n or m è 0,1,2 è 0: standard input (stdin) /
1: standard output (stdout) / 2: standard err (stderr)
:
deliver the 2(stderr) to 1(stdout)
o
|
:
run command additionally
o
tee
:
Copy to file the object of stdin/stdout ( object of stdin/stdout : build logs
in consol window )
:
Can be check the build log in consol window directly and also can be save logs
as file
Android: ADB Command Lists
1. Getting Root Permission
adb root
2. Reboot Hanset
adb shell reboot
3. Extract APK file
adb wait-for-device remount
adb pull /system/app/APK_NAME.apk "<Extracted_Path>/."
OR
adb pull /data/app/APK_NAME.apk "Extracted_Path/."
4. Show Connected Devices Lists
adb devices
List of devices attached
emulator-5554 device
emulator-5556 device
emulator-5558 device
5. Issuing Shell Commands / Select One Devices
adb -s <Serial Number> shell
For example, adb -s emulator-5556 shell
6. Install APK
adb install <path_to_apk>
7. Uninstall APK
adb shell pm uninstall com.example.MyApp
8. Get System Property
adb shell getprop
adb shell getprop <systemproperty_name>
9. Set System Property
adb shell setprop <systemproperty_name> <value>
10. Search File List
11. View LOG
adb logcat
12. Change MODEM (Baseband) Image
adb wait-for-device remount
adb push /modem_image_name_in_local/ /modem_image_path_in_ME/
For example, LENOVO Handset.
adb push modem.img /system/etc/firmware
adb shell sync
adb shell reboot
adb root
2. Reboot Hanset
adb shell reboot
3. Extract APK file
adb wait-for-device remount
adb pull /system/app/APK_NAME.apk "<Extracted_Path>/."
OR
adb pull /data/app/APK_NAME.apk "Extracted_Path/."
4. Show Connected Devices Lists
adb devices
List of devices attached
emulator-5554 device
emulator-5556 device
emulator-5558 device
5. Issuing Shell Commands / Select One Devices
adb -s <Serial Number> shell
For example, adb -s emulator-5556 shell
6. Install APK
adb install <path_to_apk>
7. Uninstall APK
adb shell pm uninstall com.example.MyApp
8. Get System Property
adb shell getprop
adb shell getprop <systemproperty_name>
9. Set System Property
adb shell setprop <systemproperty_name> <value>
10. Search File List
adb shell ls /system/bin
11. View LOG
adb logcat
12. Change MODEM (Baseband) Image
adb wait-for-device remount
adb push /modem_image_name_in_local/ /modem_image_path_in_ME/
For example, LENOVO Handset.
adb push modem.img /system/etc/firmware
adb shell sync
adb shell reboot
Android: ADB - Recovery (Factory Rest)
You can use the below ADB command to do recovery your phone (Do factory reset).
adb shell recovery --wipe_data
* The arguments which may be supplied in the recovery.command file:
* --send_intent=anystring - write the text out to recovery.intent
* --update_package=path - verify install an OTA package file
* --wipe_data - erase user data (and cache), then reboot
* --wipe_cache - wipe cache (but not user data), then reboot
* --set_encrypted_filesystem=on|off - enables / diasables encrypted fs
adb shell reboot recovery
Android: How to keep current state (Using SharedPreferences method)
1. Save Data
SharedPreferences shprefs
= getSharedPreferences((String)"GroupSMSApp", MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor preeditor = shprefs.edit();
preeditor.putString((String)"s_prefix", mPrefix);
preeditor.putString((String)"s_postfix", mPostfix);
preeditor.putString((String)"s_message", mMessage);
preeditor.commit();
2. Getting Data
SharedPreferences prefs =
getApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences((String)"GroupSMSApp", 0);
String mStrEditPrefix = prefs.getString((String)"s_prefix", "");
if(mStrEditPrefix != null)
mEditPrefix.setText(mStrEditPrefix);
String mStrEditPostfix = prefs.getString((String)"s_postfix", "");
if(mStrEditPostfix != null)
mEditPostfix.setText(mStrEditPostfix);
String mStrEditMessage = prefs.getString((String)"s_message", "");
if(mStrEditMessage != null)
mEditMessage.setText(mStrEditMessage);
3. Saved Location
data/data/PACAKGE_NAME/shared_prefs/GroupSMSApp.xml
From : http://developer.android.com
public interface
SharedPreferences
| android.content.SharedPreferences |
Class Overview
Interface for accessing and modifying preference data returned by
getSharedPreferences(String, int). For any particular set of preferences, there is a single instance of this class that all clients share. Modifications to the preferences must go through an SharedPreferences.Editor object to ensure the preference values remain in a consistent state and control when they are committed to storage. Objects that are returned from the various get methods must be treated as immutable by the application.
Note: currently this class does not support use across multiple processes. This will be added later.
Developer Guides
For more information about using SharedPreferences, read the Data Storage developer guide.
See Also
Summary
| Nested Classes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SharedPreferences.Editor | Interface used for modifying values in a SharedPreferences object. | ||||||||||
| SharedPreferences.OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener | Interface definition for a callback to be invoked when a shared preference is changed. | ||||||||||
| Public Methods | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Checks whether the preferences contains a preference.
| |||||||||||
Create a new Editor for these preferences, through which you can make modifications to the data in the preferences and atomically commit those changes back to the SharedPreferences object.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve all values from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve a boolean value from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve a float value from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve an int value from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve a long value from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve a String value from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Retrieve a set of String values from the preferences.
| |||||||||||
Registers a callback to be invoked when a change happens to a preference.
| |||||||||||
Unregisters a previous callback.
| |||||||||||
Public Methods
public abstract boolean contains (String key)
Added in API level 1
Checks whether the preferences contains a preference.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to check. |
|---|
Returns
- Returns true if the preference exists in the preferences, otherwise false.
public abstract SharedPreferences.Editor edit ()
Added in API level 1
Create a new Editor for these preferences, through which you can make modifications to the data in the preferences and atomically commit those changes back to the SharedPreferences object.
Note that you must call
commit() to have any changes you perform in the Editor actually show up in the SharedPreferences.Returns
- Returns a new instance of the
SharedPreferences.Editorinterface, allowing you to modify the values in this SharedPreferences object.
public abstract Map<String, ?> getAll ()
Added in API level 1
Retrieve all values from the preferences.
Note that you must not modify the collection returned by this method, or alter any of its contents. The consistency of your stored data is not guaranteed if you do.
Returns
- Returns a map containing a list of pairs key/value representing the preferences.
Throws
| NullPointerException |
|---|
public abstract boolean getBoolean (String key, boolean defValue)
Added in API level 1
Retrieve a boolean value from the preferences.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to retrieve. |
|---|---|
| defValue | Value to return if this preference does not exist. |
Returns
- Returns the preference value if it exists, or defValue. Throws ClassCastException if there is a preference with this name that is not a boolean.
Throws
| ClassCastException |
|---|
public abstract float getFloat (String key, float defValue)
Added in API level 1
Retrieve a float value from the preferences.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to retrieve. |
|---|---|
| defValue | Value to return if this preference does not exist. |
Returns
- Returns the preference value if it exists, or defValue. Throws ClassCastException if there is a preference with this name that is not a float.
Throws
| ClassCastException |
|---|
public abstract int getInt (String key, int defValue)
Added in API level 1
Retrieve an int value from the preferences.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to retrieve. |
|---|---|
| defValue | Value to return if this preference does not exist. |
Returns
- Returns the preference value if it exists, or defValue. Throws ClassCastException if there is a preference with this name that is not an int.
Throws
| ClassCastException |
|---|
public abstract long getLong (String key, long defValue)
Added in API level 1
Retrieve a long value from the preferences.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to retrieve. |
|---|---|
| defValue | Value to return if this preference does not exist. |
Returns
- Returns the preference value if it exists, or defValue. Throws ClassCastException if there is a preference with this name that is not a long.
Throws
| ClassCastException |
|---|
public abstract String getString (String key, String defValue)
Added in API level 1
Retrieve a String value from the preferences.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to retrieve. |
|---|---|
| defValue | Value to return if this preference does not exist. |
Returns
- Returns the preference value if it exists, or defValue. Throws ClassCastException if there is a preference with this name that is not a String.
Throws
| ClassCastException |
|---|
public abstract Set<String> getStringSet (String key, Set<String> defValues)
Added in API level 11
Retrieve a set of String values from the preferences.
Note that you must not modify the set instance returned by this call. The consistency of the stored data is not guaranteed if you do, nor is your ability to modify the instance at all.
Parameters
| key | The name of the preference to retrieve. |
|---|---|
| defValues | Values to return if this preference does not exist. |
Returns
- Returns the preference values if they exist, or defValues. Throws ClassCastException if there is a preference with this name that is not a Set.
Throws
| ClassCastException |
|---|
public abstract void registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener (SharedPreferences.OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener listener)
Added in API level 1
Registers a callback to be invoked when a change happens to a preference.
Parameters
| listener | The callback that will run. |
|---|
public abstract void unregisterOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener (SharedPreferences.OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener listener)
Added in API level 1
Unregisters a previous callback.
Parameters
| listener | The callback that should be unregistered. |
|---|
Android: How to send SMS
Add Permission into Manifest
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_SMS" />
Add API into Source
private void sendSMS(String m_phoneNumber, final String m_smsMessage)
{
String SENT = "SMS_SENT";
String DELIVERED = "SMS_DELIVERED";
Log.d(TAG, "In sendSMS()");
PendingIntent sentPI
= PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent(SENT), 0);
PendingIntent deliveredPI
= PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent(DELIVERED), 0);
Log.d(TAG, "sendTextMessage() : number = " + m_phoneNumber
+ ", Message = " + m_smsMessage);
// Write SMS data into DB
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("address", m_phoneNumber.replace("-", ""));
values.put("body", m_smsMessage);
values.put("protocol", MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT);
getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://sms/sent"), values);
// Send Text Message
SmsManager.getDefault().sendTextMessage(m_phoneNumber.replace("-", ""),
null, m_smsMessage, sentPI, deliveredPI);
}
Android: Group SMS which is based on contact group
This post is just for introduce "Group SMS" application.
Sometimes, we need to send SMS to my customer, friends or anyone.
In this case, this application can help you to send SMS to people.
We can input prefix and postfix about each contact name and message body.
For example,
Prefix : Dear
Contact Name : Victor, Crum
Postfix : .
Message Body : Thanks for your APP.
Then 2 messages will be made automatically as below.
- Dear Victor.
Thanks for your APP.
Thanks for your APP.
Finally, this messages will be sent to each person.
You can download this APP for nothing as the below path.
App Download
Android: Saving SMS data into DB
We can send the SMS by using the below API.
SmsManager.getDefault().sendTextMessage()
But it is not saved into the conversation list.
For this reason, we can't know what message is sent.
Now, I wanna let you know how to save it.
1. Add <uses-permission>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_SMS" />
2. Add Code
public class TestActivity extends Activity {
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_ALL = 0;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_INBOX = 1;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT = 2;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_DRAFT = 3;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_OUTBOX = 4;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_FAILED = 5; // for failed outgoing messages
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_QUEUED = 6; // for messages to send later
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("address", m_phoneNumber.replace("-", ""));
values.put("body", m_smsMessage);
values.put("protocol", MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT);
getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://sms/sent"), values);
In this point, "content://sms/sent" is really really important.
Please take a look at the below picture.
The left side is MT SMS and right side is MO SMS.
"content://sms/sent" : Save as MO SMS
"content://sms/inbox" : Save as MT SMS
SmsManager.getDefault().sendTextMessage()
But it is not saved into the conversation list.
For this reason, we can't know what message is sent.
Now, I wanna let you know how to save it.
1. Add <uses-permission>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SMS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_SMS" />
2. Add Code
public class TestActivity extends Activity {
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_ALL = 0;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_INBOX = 1;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT = 2;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_DRAFT = 3;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_OUTBOX = 4;
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_FAILED = 5; // for failed outgoing messages
public static final int MESSAGE_TYPE_QUEUED = 6; // for messages to send later
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("address", m_phoneNumber.replace("-", ""));
values.put("body", m_smsMessage);
values.put("protocol", MESSAGE_TYPE_SENT);
getContentResolver().insert(Uri.parse("content://sms/sent"), values);
In this point, "content://sms/sent" is really really important.
Please take a look at the below picture.
The left side is MT SMS and right side is MO SMS.
"content://sms/sent" : Save as MO SMS
"content://sms/inbox" : Save as MT SMS
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)






